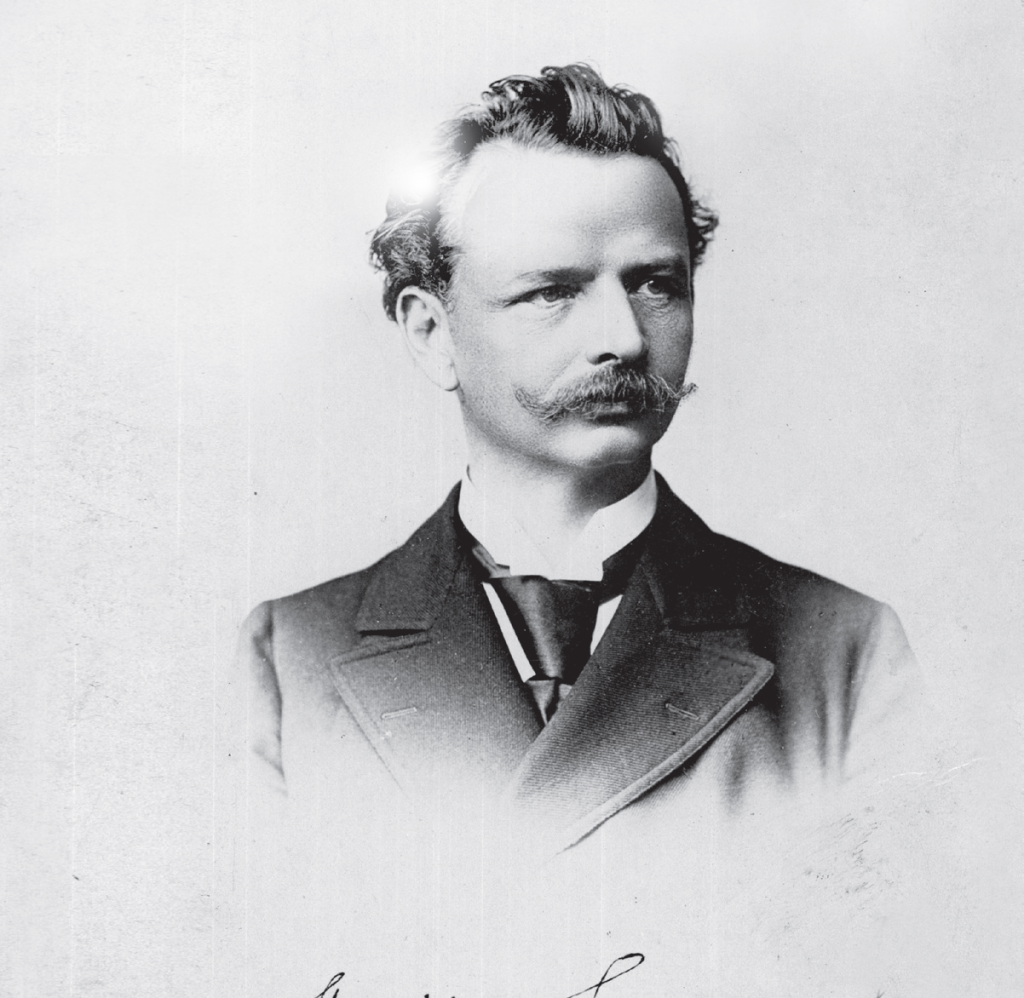
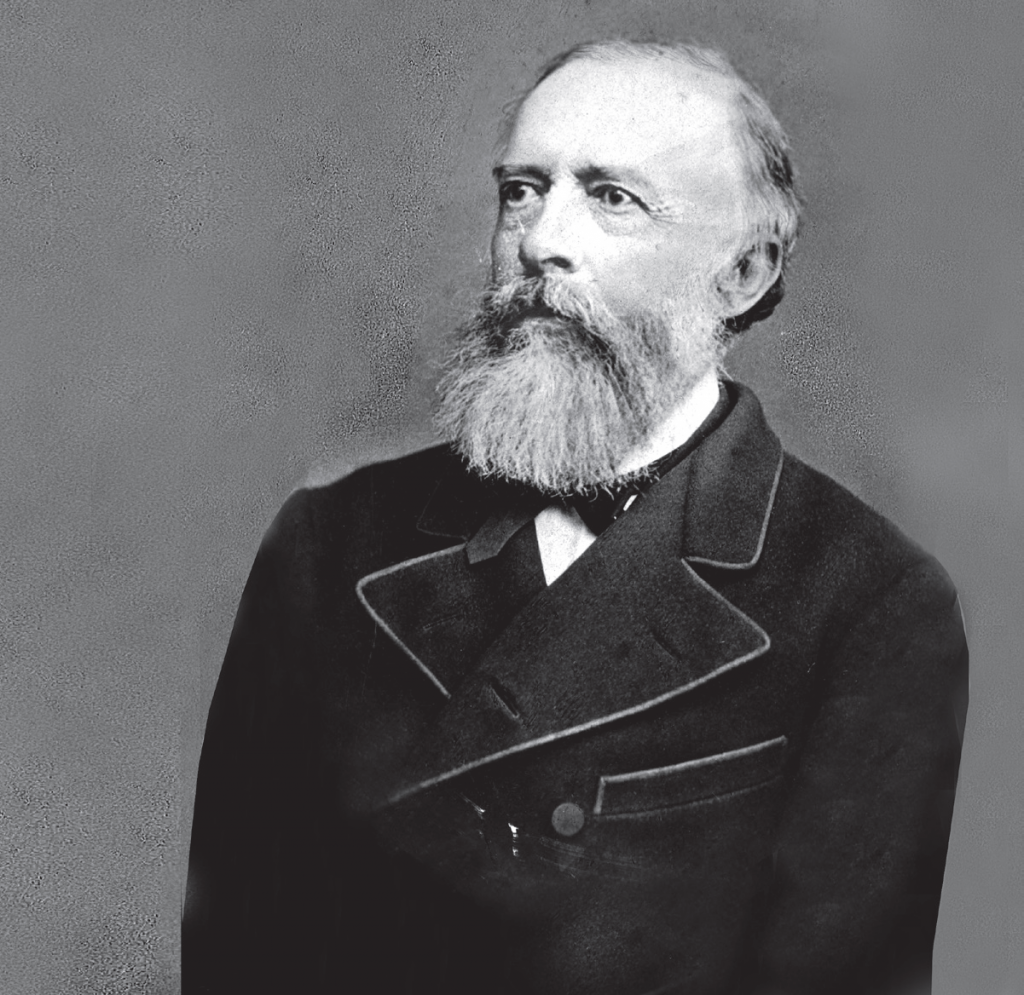As the son of a wealthy landowner, when he came of age, he received the villages of Polanka and Świerzowa. In 1853, the herd of sheep – a source of considerable income for the Polanka farm – was being decimated by an epidemic. The witch doctor brought in from Bóbrka recommended that the sheep be covered with the black goo, which was plentiful in the local waters. The treatment was unexpectedly successful and Trzecieski turned his attention towards oil. He collected it not only from the waters, but also from excavations. The oil extraction profits made Tytus Trzecieski even wealthier and let him expand as a philanthropist.
Stanisław Szczepanowski was born in Kościan, Wielkopolska, and died in Nauheim. He studied at the Vienna Institute of Technology, the École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures in Paris and studied chemical technology and economics in London. In 1877, he received British Citizenship and was invited on a business trip to India with the Prince of Wales, the heir to the throne and future British King Edward VII. Szczepanowski refused. He chose Galicia instead, where he arrived in 1879 to explore oil and with a social and economic mission. In 1879 he went to Galicia.He founded an oil mine in Słoboda Rungurska, which produced 60 percent of Galician oil. While he grew his business, Szczepanowski also developed social and political activity in Galicia. He built houses for workers, opened cooperative stores and community houses, organised vocational training, and promoted the concept of cooperativeness as the publisher of the Self-Help weekly and president of the Union of Gainful and Economic Associations.
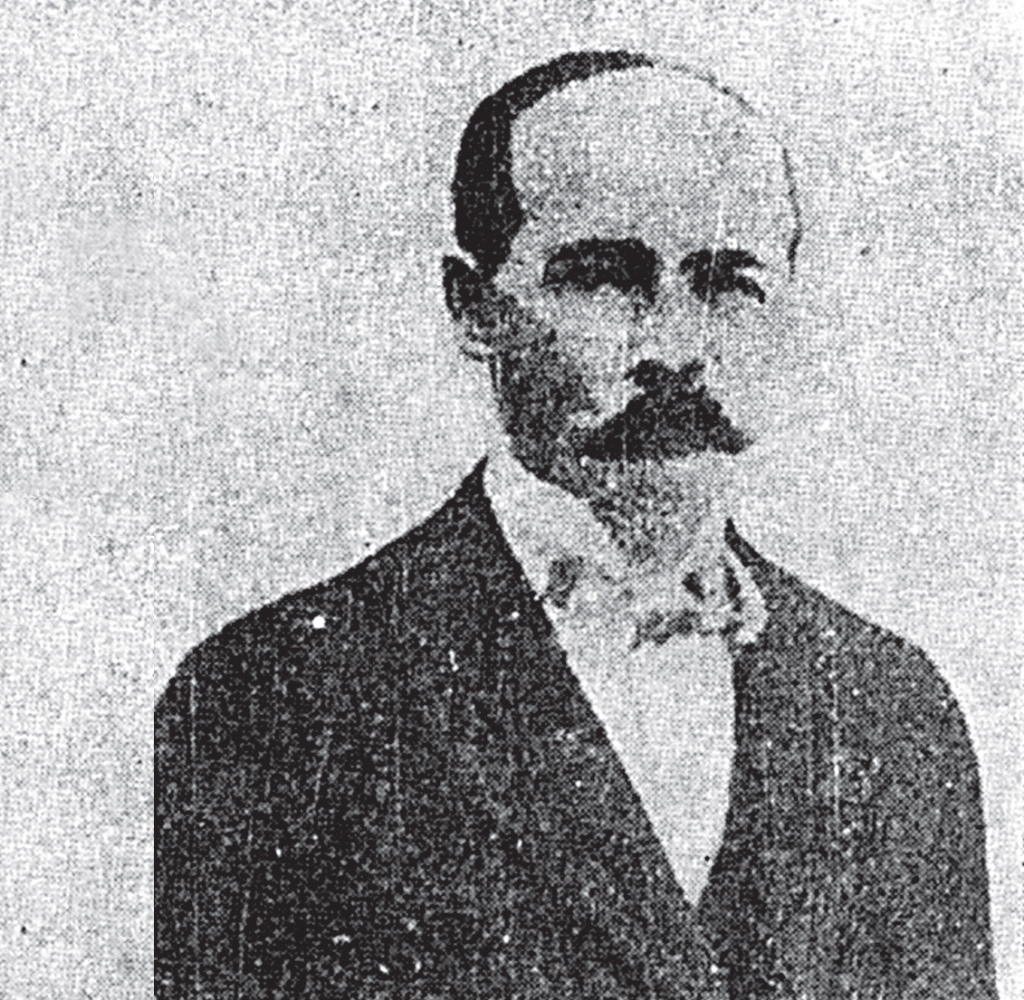
From an early age, Zenon Suszycki was interested in technology, which led him to the Faculty of Mathematics and Physics of Moscow University. He fought in the January Uprising and had to leave abroad after it was suppressed. As an emigrant in Paris, he studied at the École des mines – a mining academy – where he obtained the title of mining engineer in 1870. He returned to settle in Galicia and got involved in the development of a new industrial field, the oil industry. He got a job as manager of the oil mine in Ropianka near Dukla, where he opened Poland’s first vocational drilling school. The candidates had to meet considerable requirements – besides writing, reading, and sketching, they had to document a minimum of two years of experience working in a mine. Over the three-month-long course, the students learned the most important aspects of the machines, as well as their structure and operation. The school also promoted the new hammer drilling method.